Choose the right equipment for your needs
At EuroSensors, we pride ourselves on our thermistor expertise. With over 10 years of experience, our team of experts is here to help you find the ideal solution for your temperature measurements. We offer a wide range of high quality products to ensure the precision and accuracy of your results.
Entrust your choice to EuroSensors and benefit from a service and a material adapted to your needs.
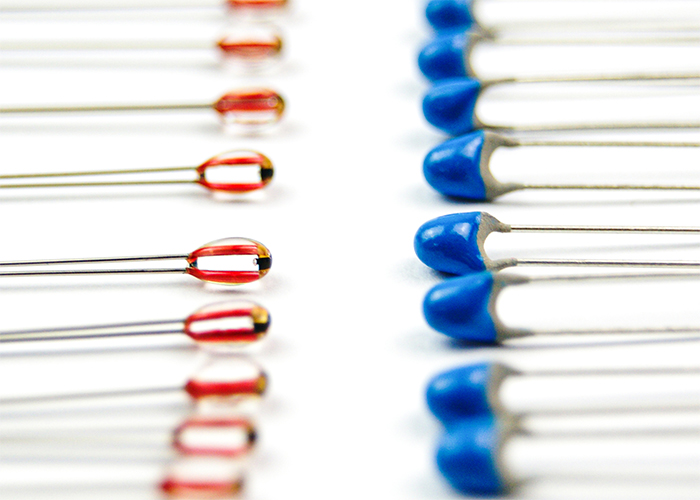
What is a thermistor?
A thermistor is an electrical component that changes its resistance according to temperature. It consists of a conductive material that is wrapped in an insulating material. As the temperature increases, the resistance of the conductive material decreases (NTC), or increases (PTC), which can be detected and measured.
Our range of thermocouples
NTC probe
Negative temperature coefficient resistors. Resistance decreases as temperature increases.
NTC probe
Positive temperature coefficient resistors. The resistance decreases as the temperature decreases.
Whatever your need, we have the solution

For large volumes
Ask for a personalized quote

For small volumes
Buy your parts on our website Heklas.com

For expert advice
Be accompanied before making a purchase

For questions
Get advice before you order
What are the two types of thermistor?
NTC thermistors (Negative Temperature Coefficient) are made of a conductive material based on transition metals and are used to measure temperatures up to 300 °C.
PTC thermistors (Positive Temperature Coefficient) are made of a conductive material based on polymer or ceramic or ceramic material and are used to measure temperatures up to 200 °C.
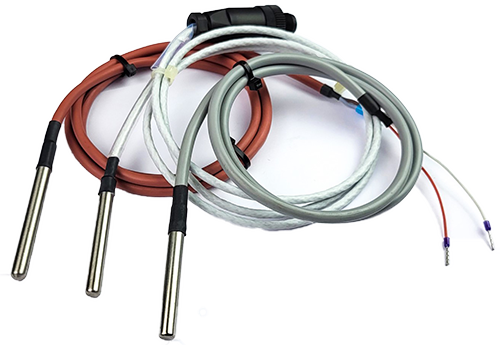
What is the difference between an NTC and a PTC?
NTCs and PTCs are both thermistors, i.e. temperature sensors that change resistance
depending on the temperature. However, There is a major difference between these two types of thermistors:
NTC thermistor
CNTs have a resistance that decreases as the temperature increases. They are commonly used in thermostats and temperature control devices to measure room temperature.
PTC thermistors
PTCs have a resistance that increases as the temperature rises. They are commonly used in thermostatic fuses and overcurrent protection devices to shut off power in the event of overheating.
How do I know if a thermistor is working?
There are several ways to tell if a thermistor (or thermal resistor) is working properly:
Resistance measurement: use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance of the thermistor at different temperatures. You can then compare these measurements to those specified by the manufacturer to verify that the thermistor is working properly.
Temperature measurement: use a thermometer or temperature measuring device to measure the temperature of the thermistor. This will allow you to verify that the thermistor is responding properly to temperature changes.
In-Circuit Testing: If the thermistor is used in a circuit, you can use a multimeter to verify that the current and voltage are correct in the circuit. If the values do not match those expected, there may be a problem with the thermistor.
Use of a measuring device: There are specific measuring devices for thermal resistors, which will allow you to measure the resistance of the thermistor and check whether it corresponds to the manufacturer’s specifications.
It is important to note that in order to perform these tests, the thermistor must be at a stable and known temperature to ensure correct results, and it must not be damaged or contaminated before testing.
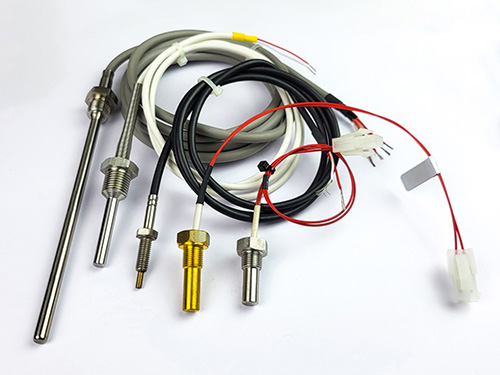

How to choose between an NTC and a PTC thermistor?
Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, so the choice will depend on your application requirements.
NTC thermistors have a resistance that decreases as the temperature increases. They are commonly used to measure low temperatures and have a relatively low cost. However, their accuracy can be affected by aging and ambient temperature variations, and they often require a compensation circuit to achieve adequate accuracy.
PTC thermistors have a resistance that increases with increasing temperature. They are commonly used to protect electronic devices from overcurrent and high temperatures. They have a good balance between accuracy and cost, and they do not need a compensation circuit to work properly. However, the triggering temperature may vary depending on the frequency of use and the ambient temperature.
Overall, it is important to consider the temperature requirements of your application, the costs, and the features required when choosing between an NTC or PTC thermistor.
If you want more details to make a choice, it is necessary to understand the important criteria such as temperature range, accuracy, stability, life span, resistance, costs and dimensions.
For which fields of application
Our thermistors are used in many sectors of activity. Here are some examples of industries that use them:

Aeronautics/space


Agri-food

Automotive


Medical


HVAC

Why choose EuroSensors?
European manufacturing
ISO 9001 certification
Manufacturer since 2010
Warranty and service
Expert advice
More than 240 customers in over 10 countries
A project ? A quote?
We will respond as soon as possible
